What is the difference between Alzheimer’s disease and dementia? This one of the most common questions asked.
Dementia is a general term that describes a set of symptoms that can be present in many different health conditions. These symptoms include difficulties with thinking, remembering, and reasoning that are severe enough to interfere with a person’s daily life.
There are many different conditions that can cause dementia. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause. It is a progressive disease of the brain. One of the most common early symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease is having trouble with short-term memory. This can cause difficulty remembering newly learned information such as appointments or recent conversations. As the disease progresses, issues with communication, planning, judgment, mood, behavior, and confusion about time and place can occur.
Here is an analogy to help clarify the difference between Alzheimer’s and dementia:
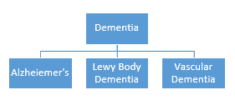
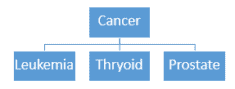
See the below picture: Dementia is a general term with many specific types including Alzheimer’s disease, Lewy body, and vascular. In a similar way, cancer is a general term with specific types such as leukemia, thyroid, and prostate.
It is important to note that dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, results because of damage to the brain; therefore, individuals are not choosing to have issues with communication, planning, judgment, mood, behavior, etc. These behaviors are happening because of changes in their brain.
We need to show compassion and support to individuals with dementia.
If you would like more information about the supports, resources, and education available related to dementia, contact your local Aging & Disability Resource Center by calling 800-514-0066. Know you are not alone!